An application server is a set of executables that collectively interpret the ABAP/4 programs and manage the input and output for them.
All requests that come in from presentation servers are directed first to the dispatcher.
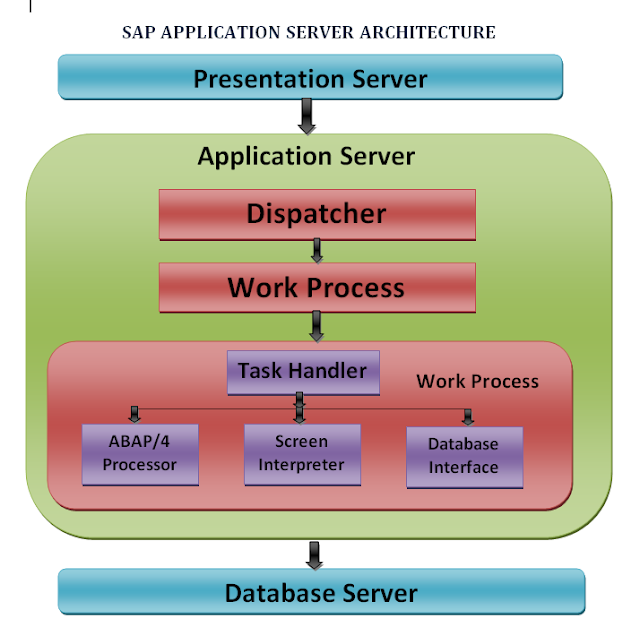
Dispatcher:
- The dispatcher is the link between the work processes and the users logged onto the application server.
- The dispatcher writes the task first to the dispatcher queue.
- The dispatcher pulls the requests from the queue on a first-in, first-out basis.
- Each request is then allocated to the first available work process.
Work process:
- An application server contains work processes, which are components that can run an application
- It handles one request at a time.
- To perform any processing for a user’s request, a work process needs to address two special memory areas:
2. The program roll area- It is a memory area that contains information about the programs execution.
Understanding a User Context:
- A user context is memory that is allocated to contain the characteristics of a user that is logged on the R/3 system.
- It holds information needed by R/3 about the user, such as:
- The user’s current settings
- The user’s authorizations
- The names of the programs the user is currently running
- When a user logs on, a it is allocated for that logon. When they log off, it is freed.
Understanding a Roll Area:
- A roll area is memory that is allocated by a work process for an instance of a program.
- It holds information needed by R/3 about the program’s execution, such as:
- The values of the variables
- The dynamic memory allocations
- The current program pointer
- Each time a user starts a program, a roll area is created for that instance of the program.
- If two users run the same program at the same time, two roll areas will exist-one for each user. The roll area is freed when the program ends.
Types of Work Processes:
- There are seven types of work processes.
- Each handles a specific type of request.
- The type of work processes and the types of requests that they handle are shown in Table.
WP Type
|
Request Type
|
D (Dialog)
|
· Dialog requests
· Deals with requests from an active user to execute dialog steps.
· Responsible for user interaction in the SAP R/3 interface.
· Sends user req to db and displays output of req to the user
|
V (Update)
|
· Requests to update data in the database.
· Responsible for consistency in asynchronous data changes.
|
B (Background)
|
· Background jobs
· It process programs that can be executed without user interaction ie in background at a specific time.
|
S (Spool)
|
· Print spool requests for printing job.
· It contains information about printer and the printing format.
|
E (Enqueue)
|
· Logical lock requests.
· It administers a lock table in the shared memory area.
· It manages simultaneous database access my multiple application servers.
|
M (Message)
|
· Routes messages between application servers within an R/3 system.
· Used for Logon purpose and load balancing.
|
G (Gateway)
|
· Funnels messages into and out of the R/3 system.
· Used for transport of bigger amount of data between application servers as well as external (non SAP) systems that communicates with SAP.
|
Components of a Work Process:
- Each work process is composed of the following:
- A task handler - All requests pass through the task handler, which then funnels the request to the appropriate part of the work process
- An ABAP/4 Processor - interprets and executes the ABAP/4 Programs.
- A screen interpreter - controls a large part of the user interaction. The R/3 Basis system contains a special language for programming screen flow logic. The screen processor executes the screen flow logic.
- A database interface - handles the job of communicating with the database.

